About Vitecoin

Vite is based on the Directed Acrylic Graph (DAG). "DAG will be used for applications that require scalability in thousands of transactions per second. Launching CryptoKitties clogs the Ethereum network which results in slow transactions and high costs. Ethereum has a solution for this called sharding, but it is 5 years out. The application will, I think, be switch to DAG to scale. "[2]
What is a DAG?
First let's determine the Blockchain. The Blockchain is a decentralized ledger. DAG is also a distributed decentralized ledger. DAG does the same thing as the blockchain does. The purpose of DAG is the same as the blockchain, which is to maintain a decentralized online transaction record, but DAGs achieve the same goals through different technologies. Both DAG and Blockchain are different technologies that try to achieve the same goal. There is absolutely no connection between the two technologies which limits the goals they want to achieve, namely measurable decentralized ledgers.
What is asynchronous DAG?
All DAGs are out of sync.
Why is asynchronous DAG important for blockchain technology?
Why is asynchronous DAG important for blockchain technology?
Asynchronous DAG technology is important and superior to blockchain technology because it can reach more than 100k transactions per second which is far more than the current blockchain does.
The difference between synchronous and asynchronous?
When you run something simultaneously, you wait until it's finished before moving to another task.
When you run something asynchronously, you can proceed to another task before it's finished.
When you run something simultaneously, you wait until it's finished before moving to another task.
When you run something asynchronously, you can proceed to another task before it's finished.
What does this mean for the Blockchain?
On the blockchain, new transactions are processed only after the transaction was previously confirmed. For example. All transactions in Bitcoin are first placed in a Mempool and then the miner takes transactions from there and verifies them. Miners take new transactions only after the transaction was previously verified. This is synchronous, meaning that the miner moves to the next task after completing the previous task (the task here means processing the transaction) but in DAG technology that is out of sync, all transactions are processed simultaneously even before the transaction was previously confirmed or not. This is asynchronous, meaning the validator moves to another task even before completing the previous task (the task here means processing the transaction).

What does this mean for the Blockchain?
On the blockchain, new transactions are processed only after the transaction was previously confirmed. For example. All transactions in Bitcoin are first placed in a Mempool and then the miner takes transactions from there and verifies them. Miners take new transactions only after the transaction was previously verified. This is synchronous, meaning that the miner moves to the next task after completing the previous task (the task here means processing the transaction) but in DAG technology that is out of sync, all transactions are processed simultaneously even before the transaction was previously confirmed or not. This is asynchronous, meaning the validator moves to another task even before completing the previous task (the task here means processing the transaction).
ICO VITE Review
bitcoinstartrek (34) periodically • last month
bitcoinstartrek (34) periodically • last month
ICO Vite Reviews
by Zebra Crossing
What is Vite? Vite is the Next Generation Decentralized High Performance Application Platform [1]. Vite is based on the Directed Acrylic Graph (DAG). "DAG will be used for applications that require scalability in thousands of transactions per second. Launching CryptoKitties clogs the Ethereum network which results in slow transactions and high costs. Ethereum has a solution for this called sharding, but it is 5 years out. The application will, I think, be switch to DAG to scale. "[2]
by Zebra Crossing
What is Vite? Vite is the Next Generation Decentralized High Performance Application Platform [1]. Vite is based on the Directed Acrylic Graph (DAG). "DAG will be used for applications that require scalability in thousands of transactions per second. Launching CryptoKitties clogs the Ethereum network which results in slow transactions and high costs. Ethereum has a solution for this called sharding, but it is 5 years out. The application will, I think, be switch to DAG to scale. "[2]
What is a DAG?
First let's determine the Blockchain. The Blockchain is a decentralized ledger. DAG is also a distributed decentralized ledger. DAG does the same thing as the blockchain does. The purpose of DAG is the same as the blockchain, which is to maintain a decentralized online transaction record, but DAGs achieve the same goals through different technologies. Both DAG and Blockchain are different technologies that try to achieve the same goal. There is absolutely no connection between the two technologies which limits the goals they want to achieve, namely measurable decentralized ledgers.
What is asynchronous DAG?
All DAGs are out of sync.
Why is asynchronous DAG important for blockchain technology?
Asynchronous DAG technology is important and superior to blockchain technology because it can reach more than 100k transactions per second which is far more than the current blockchain does.
The difference between synchronous and asynchronous?
When you run something simultaneously, you wait until it's finished before moving to another task.
When you run something asynchronously, you can proceed to another task before it's finished.
When you run something asynchronously, you can proceed to another task before it's finished.
What does this mean for the Blockchain?
On the blockchain, new transactions are processed only after the transaction was previously confirmed. For example. All transactions in Bitcoin are first placed in a Mempool and then the miner takes transactions from there and verifies them. Miners take new transactions only after the transaction was previously verified. This is synchronous, meaning that the miner moves to the next task after completing the previous task (the task here means processing the transaction) but in DAG technology that is out of sync, all transactions are processed simultaneously even before the transaction was previously confirmed or not. This is asynchronous, meaning the validator moves to another task even before completing the previous task (the task here means processing the transaction).
What's so special about VITE?
Vite uses the same Lattice DAG Block as Nano but there are several security gaps in the DAG Block Lattice. They will create a snapshot chain to fix security problems with Nano DAG. And you can make a smart contract on VITE with the language Soliditas ++ (which is compatible with Soliditas). There are not many differences in Solidity and Solidity. That is why the Ethereum application is compatible with VITE. Vite's competitor is Fantom (DAG + Smart contract platform). But Fantom uses Scala language for smart contracts so Ethereum Dapps is not compatible with Fantom.
In short, VITE uses Nano DAG technology and adds smart contracts to it, plus using the Solidity ++ smart language that is compatible with Solidity.
In short, VITE uses Nano DAG technology and adds smart contracts to it, plus using the Solidity ++ smart language that is compatible with Solidity.
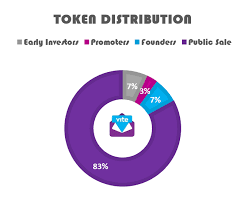
Token Distribution
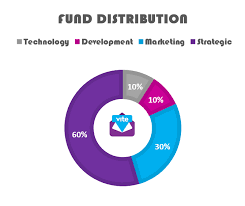
For questions about Vite, click the link below:
Website: https://www.vite.org
Whitepaper: https://www.vite.org/whitepaper/vite_en.pdf
Author by: thiokoentjoan123
https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1091812
Komentar
Posting Komentar